CT computerized axial tomography in Cosenza
CT (computed axial tomography also indicated by the acronym Tc) is a diagnostic imaging method that uses ionizing radiation (X-rays) and allows the reproduction of sections or layers (tomography) of the patient's body by carrying out three-dimensional processing.
It is particularly useful in the study of skeletal structures although, for some joints (shoulder, elbow, wrist, hand, knee, foot), it is preferable to use magnetic resonance imaging. The use of CT becomes essential to analyze fractures or their outcomes (to evaluate, for example, the position of fracture fragments).
It is also used to visualize the effects of head trauma, with particular attention to the presence of any hemorrhages and in the oncology field, in the evaluation of tumors.
The innovation of TAC with TC General Electric
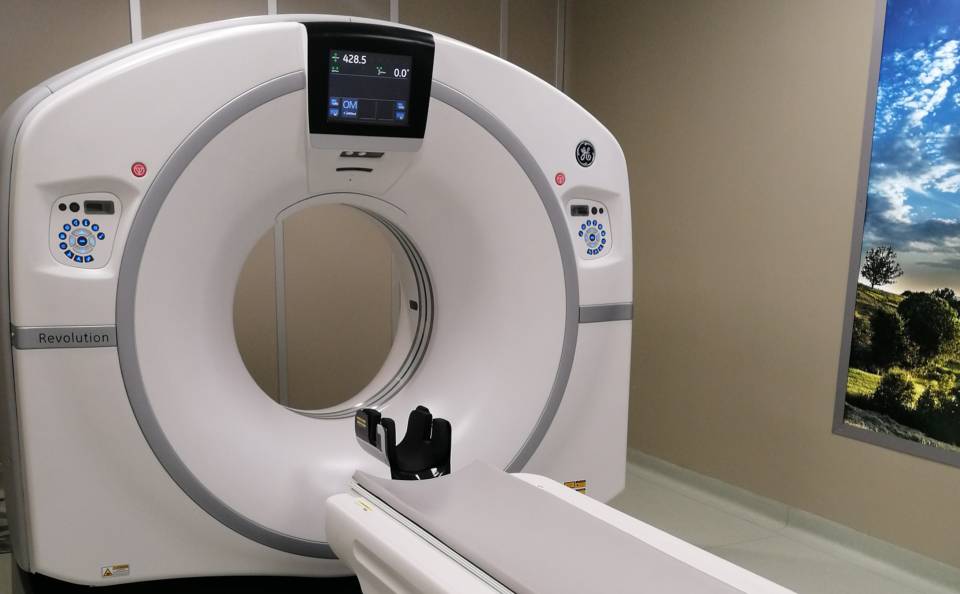
The CT scan we have (GE Revolution EVO model) is designed to support the problems of patients with complex trauma or cardiac problems and those of obese patients. The machine is equipped with various radiation dose reduction functions. A "humanization" panel placed in the diagnostics and depicting a suggestive landscape, relaxes the patient, facilitating the execution of the exam in complete relaxation. The ASIR iterative reconstruction technique, with which the system is supplied, is designed to reduce the levels of noise and the technologies it is equipped with allow it to guarantee low levels of radiation and quality diagnostic images.
Information
Computed tomography is usually necessary following x-rays or ultrasounds, or other specialist visits, to delve deeper into the patient's clinical picture.
In particular, computed tomography is used to search for primary tumors or secondary localizations, to study the central nervous system but also the vascular system, in particular the arteries. The main areas of application of computed tomography, therefore, are neurological, skeletal, traumatological, oncological, gynecological, vascular, but the CT scan is also useful for the study of the digestive and urinary systems. Finally, computed tomography is widely used in emergency conditions, for example following cerebral hemorrhages or ischemia, aneurysms, embolisms.
Furthermore, those who suffer from claustrophobia can undergo computerized tomography: the tunnel, in fact, is wide and short.
Speaking of radiation, this can even exceed 40-50 times that needed in a common x-ray: therefore it is important that the circumstances expressly require this examination. In any case, the maximum dose of radiation emitted is significantly lower than that which could cause harm to the patient.